Motherboard vendors have rolled out firmware enabling Intel’s official power limits that are usually bypassed even at factory settings. As reported back in 2021, the 13th Gen “K-series” unlocked processors have a base TDP of 125W (PL1) and a boost limit of 253W (PL2). The CPUs are meant to run at the elevated “PL2” power limit for 56 seconds (Tau) which usually corresponds to its peak single-core boost clock.
Note: The CPU used by Uniko is a Qualification Sample, but it attains the same clocks and power values as our own unit.
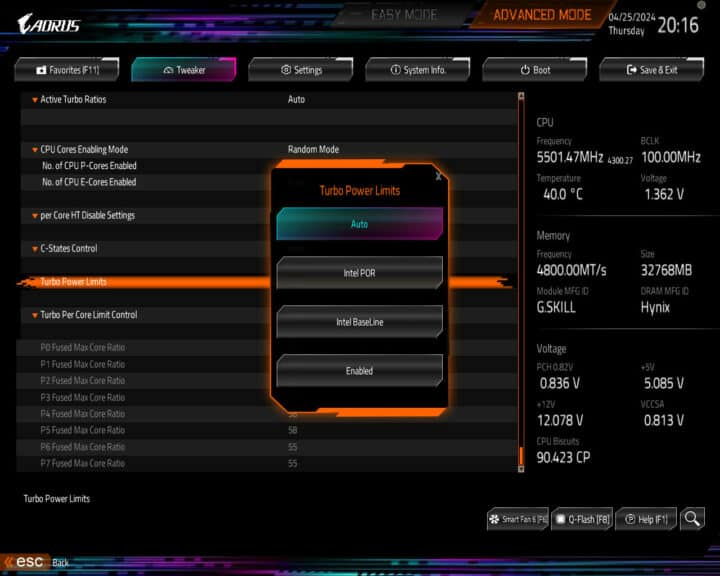
However, motherboard vendors set PL1 and PL2 to “unlimited,” uncapping any or all power restrictions. This is the case even at the factory “Auto” BIOS settings. As you can see in the above screenshot, Gigabyte has added an “Intel Baseline” power profile that restricts the boost power limits to Intel’s official spec.
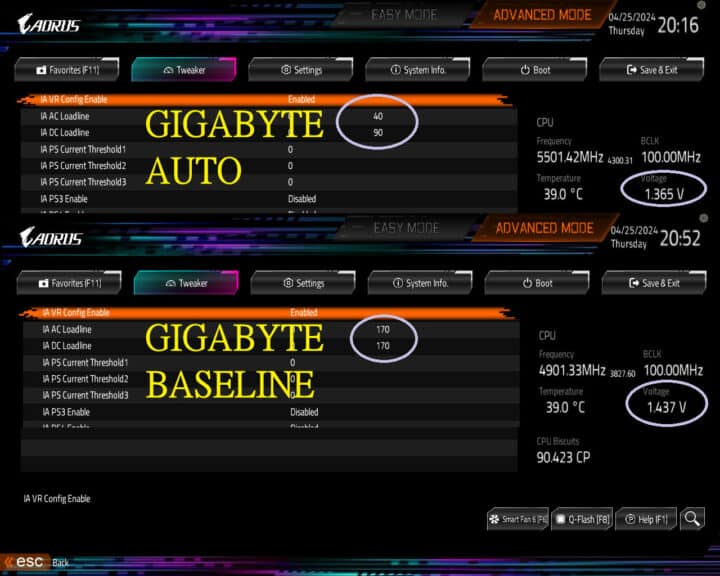
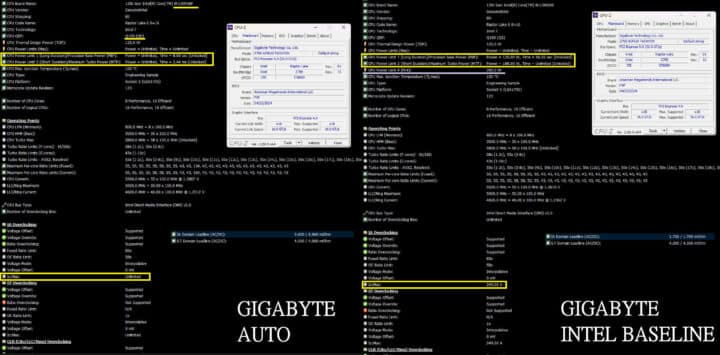
The Core i9-13900KF (as tested by Uniko’s Hardware) clocks at 5.5GHz (voltage: 1.365v) while in the BIOS using the “Auto” settings. Switching to the Intel spec increases the voltage to 1.437v despite reducing the clocks to 4.9GHz. It reduces the PL2 “Turbo” power limit to 188W while adding a PL4 limit of 293W. The latter is the “absolute max” power limit of the CPU which can’t be exceeded to prevent damage.
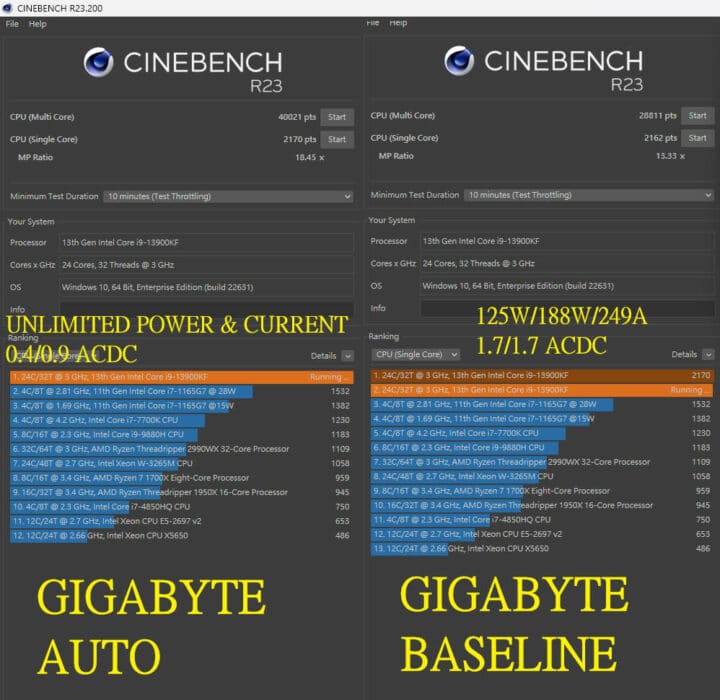
Following the implementation of the Intel baseline profile, a performance drop of up to nearly 30% can be observed in power-intensive multi-threaded workloads. Cinebench R23 is a benchmark where the multi-core score drops from 40,021 to 28,811 points. Lightly threaded workloads are largely unaffected as is the single-core score.
Gaming workloads see a modest decline in performance, mostly in the 5-10% range. This is because most games don’t push the power consumption past the official Intel spec. Consequently, even at the official Intel power specifications, the 13th and 14th Gen CPUs can boost to their marketed boost clocks (or very close to them).
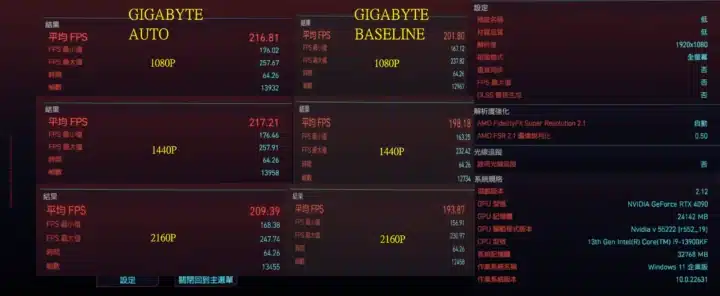
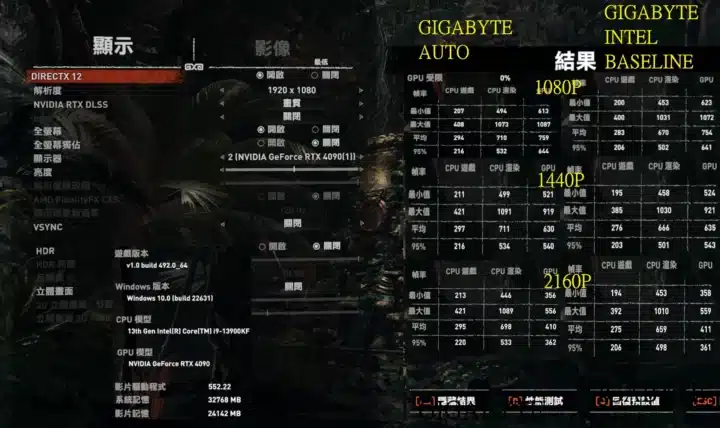

Source: Uniko’s Hardware.
14th Gen Core CPUs 10%+ Slower with Intel’s Spec Power Limits, Falls Behind the Ryzen 9 7950X

 AMD Zen 5 Strix Halo Specs: Console-Level GPU with 2560 Cores, 32MB MALL & 16 Channel LPDDR5 Memory
AMD Zen 5 Strix Halo Specs: Console-Level GPU with 2560 Cores, 32MB MALL & 16 Channel LPDDR5 Memory AMD Zen 5 CPUs Allegedly Going to Offer Only 10% IPC Uplift, Claims Lenovo Manager
AMD Zen 5 CPUs Allegedly Going to Offer Only 10% IPC Uplift, Claims Lenovo Manager AMD’s Ryzen Desktop CPU Market Share Grows by 21% in Q1 2024; Mobile/Server Flat
AMD’s Ryzen Desktop CPU Market Share Grows by 21% in Q1 2024; Mobile/Server Flat Intel on Crashing CPUs: Baseline Settings Not Suggested for Core i9-13900K/14900K
Intel on Crashing CPUs: Baseline Settings Not Suggested for Core i9-13900K/14900K