AMD has confirmed the core details of its upcoming RDNA 3 graphics architecture set to power the Radeon RX 7900 XT, 7800 XT, and 7700 XT. The chipmaker affirmed most leaks and rumors. It looks like the Navi 3x family will indeed leverage a chiplet design with a 5nm GCD (Graphics Compute Die), redesigned Compute Unit, and improved Infinity Cache (L3) architectures.
The graphics pipeline has also been optimized and that could mean a lot of things from the frontend to the backend. Overall, AMD promises a 50% performance/watt increase over RDNA 2. The 5nm process, improved graphics architecture, and L3 cache will be the primary drivers behind this increase. Let’s have a look at what we already know about the RDNA 3 lineup:
RDNA 3 will once again overhaul the Compute Unit, stuffing as many as 128 shaders across four SIMD32 units. The Work Group Processor, in turn, packs a total of 256 stream processors across eight SIMDs. As we know, AMD switched to a shorter 32 thread dispatch with RDNA, down from 64 on GCN. Known as wave32, it schedules 32 work items per SIMD for a total of 32 x2 per CU and 32 x4 per WGP.
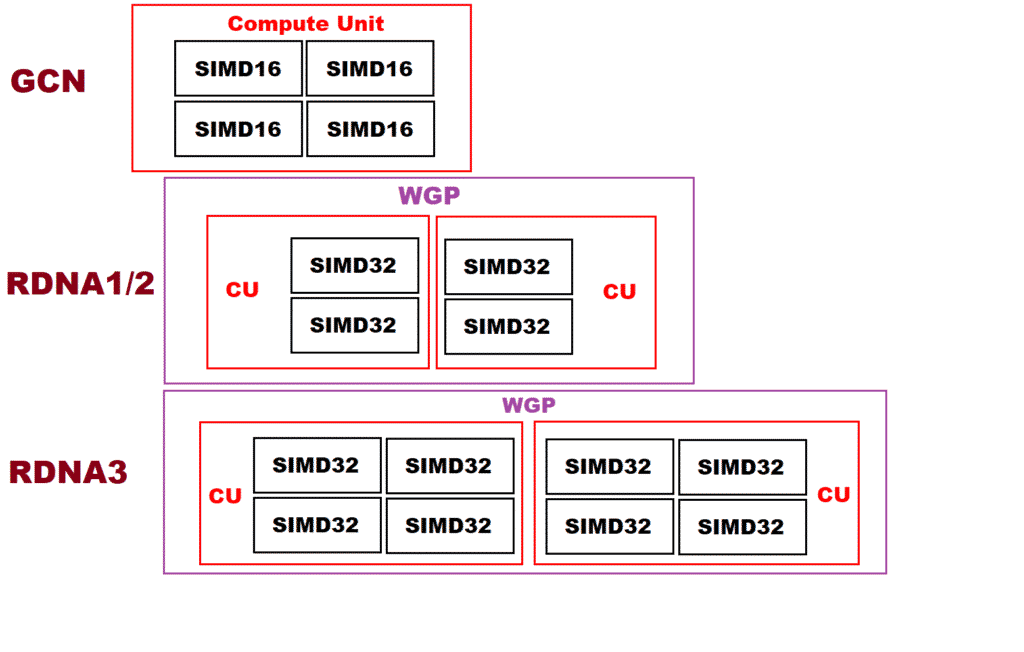
The whole point of this shakeup was the improve utilization and maximize the number of data sets being scheduled. With GCN, each Compute Unit would work on four 64-item waves, not one 64-item wave. Like Bulldozer, the aim was to maximize parallelization. At the same time, GCN wasn’t an out-of-order architecture. The instructions within a wavefront were still executed as per their order. The only advantage was that the CU or SIMDs could switch to any of the four available waves.
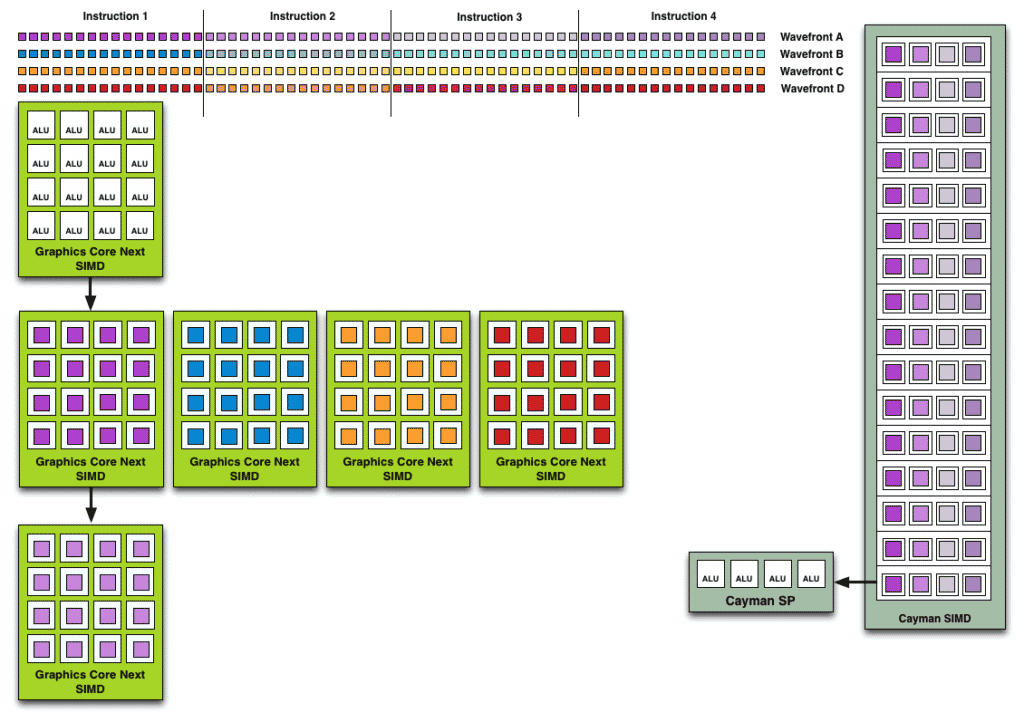
The reason why this wasn’t very effective is that most games use shorter work queues due to which only one or two out of the four wavefronts were saturated per execution cycle. As a result, AMD’s GCN scheduler had to wait for four cycles for the next wave despite having room for additional wavefronts. RDNA fixes this by reducing the wave size, and increasing the wave count. RDNA 3 doubles down on this by literally doubling the number of concurrent 32-item waves per CU and WGP.
AMD’s Radeon RX 7900 XT graphics card will be the first GPU to feature a chiplet design with up to seven dies. Contrary to prior rumors, there will be only one 5nm compute die (GCD) packing a total of 12,288 shaders across 96 compute units (CUs) or 48 Workgroup Processors (WGPs). The remaining six dies will be 6nm MCDs which is short for either Memory Complex Dies or Memory Controller Dies.
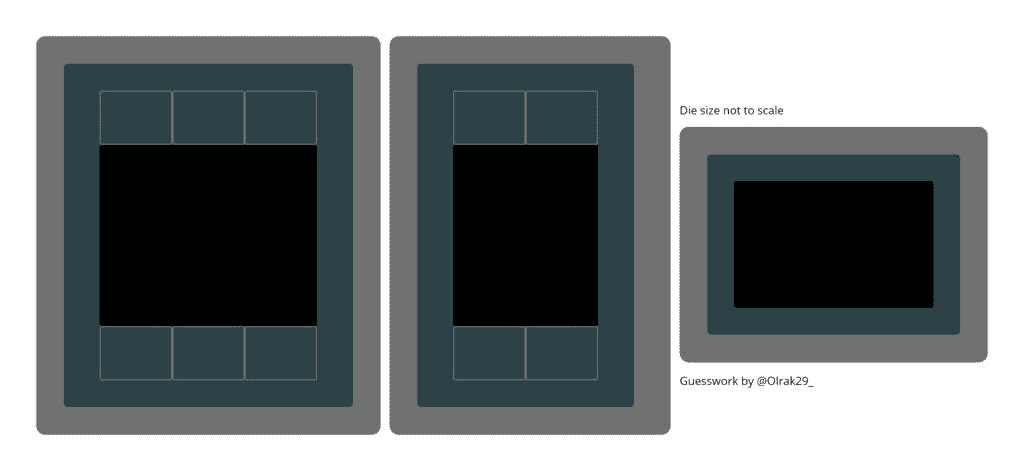
The 6nm MCDs should contain the L3 “Infinity” cache. The top-end Navi 31 GPU powering the RX 7900 XT is expected to pack between 256-512MB of last-level cache. The RX 7800 XT (Navi 32) reduces it to 128-1920MB across four MCDs while the RX 7700 XT will be a monolithic design with 64MB of cache.